In the world of business, keeping track of financial transactions is crucial for the success and growth of a company. An accounting ledger serves as the backbone of financial reporting and analysis, providing a comprehensive and organized record of all the financial activities undertaken by a business.
Table of Contents
This essential tool acts as a central repository for financial data, ensuring accuracy, and facilitating the preparation of financial statements like the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
What is an Accounting Ledger?
An accounting ledger is a record that tracks all of a business’s financial transactions, organized by account. It provides a clear and structured history of the company’s financial activity.
Each entry includes the date, transaction details, amounts debited or credited, and the relevant accounts.
The main purpose of the ledger is to organize financial data, making it easier to monitor cash flow, evaluate performance, and prepare accurate financial statements. It supports informed decision-making and ensures compliance with accounting standards.
Why Do You Need It?
The accounting ledger is essential for several reasons:
- It provides a clear and detailed record of all financial transactions, helping to track income and expenses accurately.
- It serves as the foundation for financial reporting, ensuring that the financial statements are prepared correctly.
- It helps in analyzing the financial health of the business, identifying trends, and making informed decisions.
- It facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements and auditing processes.
- It enables stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and management, to assess the company’s performance and make strategic decisions.
The Difference Between a Journal And a Ledger
Journals and ledgers serve different roles in accounting. A journal records financial transactions in chronological order as they occur. In contrast, a ledger groups these transactions into specific accounts like assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. This organization helps businesses analyze and report their financial activities more effectively.
5 Types of Accounts Found in an Accounting Ledger
1. Asset Accounts
Asset accounts track what a business owns, including cash, inventory, property, and equipment. These accounts are divided into current assets (short-term) and non-current assets (long-term).
Assets are essential for running the business and generating revenue. Cash covers daily expenses, inventory holds products for sale, and equipment supports operations. Recording assets in the ledger helps businesses monitor their financial position, manage cash flow, and make informed decisions about resource use.
2. Liability Accounts
Liability accounts track what a business owes, such as loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses. These liabilities are classified as current (short-term) or non-current (long-term).
They represent the company’s financial obligations to creditors and suppliers. Loans must be repaid over time, accounts payable cover unpaid purchases, and accrued expenses reflect costs that have been incurred but not yet paid. Recording liabilities in the ledger helps businesses manage debt, monitor obligations, and assess their ability to meet financial responsibilities.
3. Equity Accounts
Equity accounts show the ownership interest in a business, including common stock and retained earnings. They represent the company’s net worth and help assess its financial position.
These accounts reflect the owners’ claims on assets. Common stock indicates shareholder ownership, while retained earnings show accumulated profits. Tracking equity in the ledger helps evaluate net worth, monitor shareholder equity, and measure long-term financial performance.
4. Revenue Accounts
Revenue accounts track the income a business earns through its operations, including sales revenue and service revenue. These accounts reflect the company’s earnings and play a key role in measuring profitability.
Sales revenue comes from selling products, while service revenue is generated by providing services. Recording revenue in the ledger allows businesses to evaluate performance, monitor income sources, and identify areas for growth.
5. Expense Accounts
Expense accounts track the costs a business incurs to generate revenue, including salaries, rent, utilities, and advertising. They reveal where money is spent and are essential for measuring profitability.
These accounts reflect operating expenses like employee wages, office space, and support services. Recording expenses in the ledger helps businesses monitor spending, control costs, and assess profitability by comparing expenses against revenue.
The Role of the Accounting Ledger
The accounting ledger plays a vital role in the financial management of a business:
- It helps in recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions accurately.
- It provides a clear and detailed record of all financial activities, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- It facilitates the preparation of financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
- It serves as a tool for analyzing the financial performance of the business, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and making informed decisions.
The Components of an Accounting Ledger
An accounting ledger includes several key components that help organize and track financial transactions accurately:
- Account Titles: Each account is labeled with a specific title that reflects the type of transactions it records, such as Cash, Accounts Receivable, or Utilities Expense.
- Date: Every transaction is recorded with the exact date it occurred, ensuring entries are listed in chronological order for accurate tracking and reference.
- Description: A short explanation or note is included with each transaction to clarify the nature or purpose of the entry.
- Debit and Credit Columns: The ledger uses separate columns for debits and credits, in line with double-entry accounting, where every transaction affects at least two accounts.
- Running Balance: Each account in the ledger shows a running balance that updates with every transaction, allowing users to see the cumulative financial position over time.
How to Write a Ledger
Writing a ledger involves the following steps:
1. Identify the Accounts to be Included
Before creating a ledger, businesses must identify the accounts they need to include. These typically cover five main categories: assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. Each account should be titled and assigned to a specific type of transaction. This setup ensures accurate, organized, and consistent recordkeeping across all financial activities.
2. Record Each Financial Transaction
Once the accounts are set up, businesses can start recording financial transactions in the ledger. Each entry should include the date, a short description, the debit or credit amount, and the appropriate account titles. Following double-entry accounting rules is essential, ensuring that every transaction has equal debits and credits to keep the books balanced.
3. Calculate the Balance of Each Account
After recording transactions in the ledger, businesses need to calculate the balance of each account. This involves totaling the debits and credits for each account and determining the account’s ending balance. The balance should reflect the cumulative effect of all transactions recorded in the account up to that point.
4. Update the Ledger Regularly
It is important to update the ledger regularly with new transactions as they occur. By keeping the ledger current and accurate, businesses can track their financial activities in real-time and make informed decisions based on up-to-date information. Regular updates also ensure that the ledger remains organized, reliable, and comprehensive for financial reporting and analysis purposes.
5. Ensure Accuracy and Consistency
Accuracy and consistency are key principles in maintaining an accounting ledger. Businesses should double-check entries for errors, reconcile balances regularly, and ensure that transactions are recorded correctly. Consistency in recording transactions and following accounting principles ensures that the ledger provides a reliable and verifiable record of the company’s financial activities.
6. Utilize Accounting Software
Many businesses use accounting software to maintain their accounting ledgers efficiently. Accounting software automates the recording of transactions, calculations of balances, and generation of reports, saving time and reducing the risk of errors. By leveraging accounting software, businesses can streamline their accounting processes, improve accuracy, and access valuable financial insights for decision-making.
7. Seek Professional Guidance
For businesses that are new to accounting or require assistance in maintaining their accounting ledgers, seeking professional guidance is advisable. Professional accountants can provide expertise, guidance, and support in setting up and managing accounting ledgers effectively. They can offer insights on best practices, compliance with accounting standards, and optimization of accounting processes to ensure accurate and reliable financial reporting.
8. Conduct Regular Reconciliations
Regular reconciliations are essential to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the accounting ledger. Businesses should compare the balances in the ledger with other financial records, such as bank statements, invoices, and receipts. Reconciliations help identify discrepancies, errors, or fraudulent activities that may impact the reliability of the ledger’s data. By conducting regular reconciliations, businesses can maintain the trustworthiness of their financial information.
9. Implement Internal Controls
Internal controls are measures that help protect assets, prevent fraud, and ensure accurate financial records. Businesses should build internal controls into their accounting systems to maintain the integrity of the ledger. These controls can include separating duties, requiring proper authorization, and limiting access so that only approved personnel can update the ledger. With strong internal controls, businesses reduce the risk of errors, fraud, and financial misstatements.
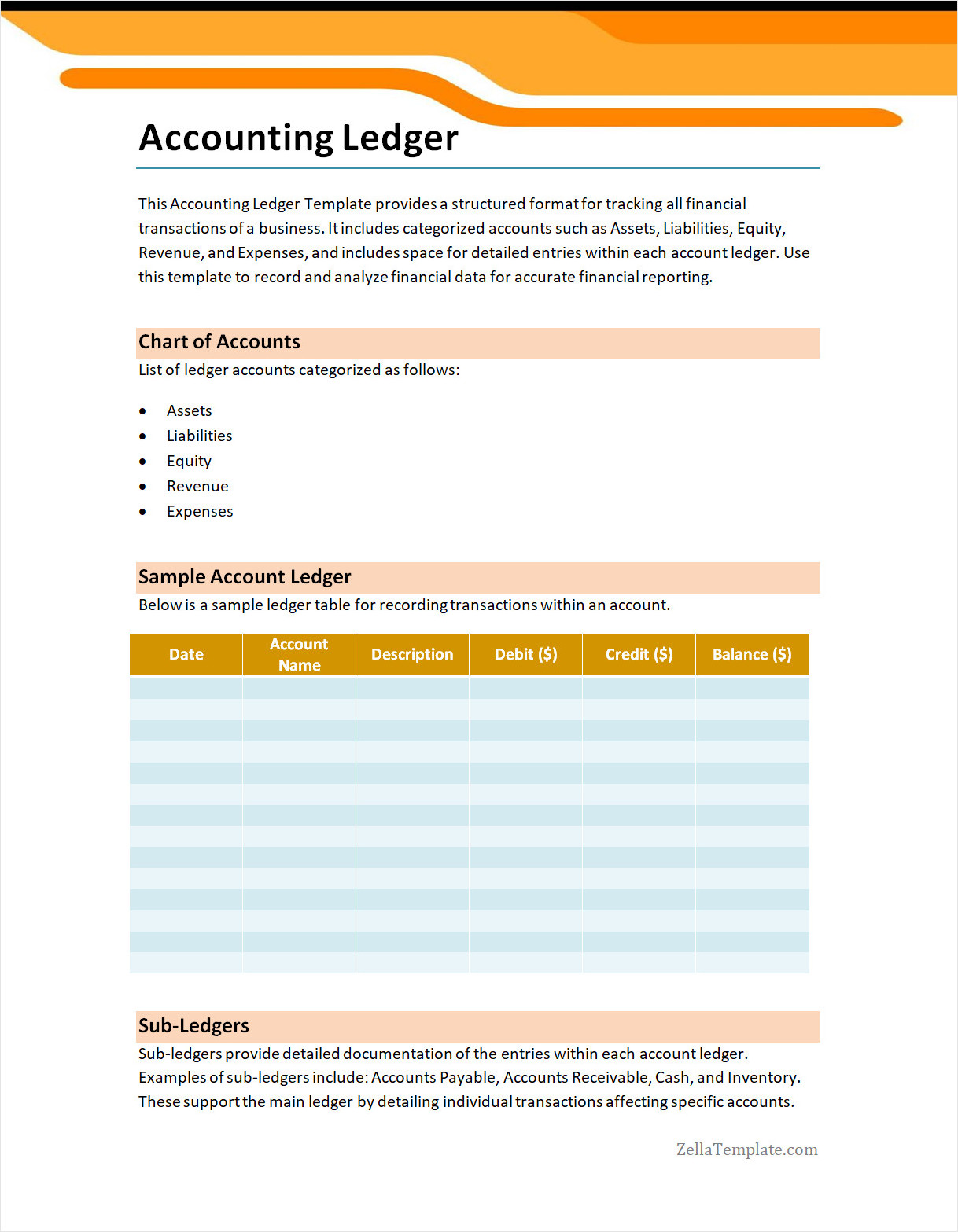
Accounting Ledger Template
An accounting ledger is a vital tool for tracking income, expenses, and financial transactions with accuracy and clarity. Whether you’re managing a small business, freelancing, or keeping personal finances in order, a structured ledger helps you stay organized and make informed financial decisions.
Use our free accounting ledger template today to take control of your finances with ease. Simple to use, fully customizable, and perfect for businesses, individuals, and bookkeepers alike.
Accounting Ledger Template – Word