What Is a Bill of Lading?
A bill of lading is a key document in shipping that serves as a receipt, contract, and legal proof of goods in transit. It lists details like the type, quantity, and destination of the cargo. It confirms the carrier received the goods and outlines the shipper’s and carrier’s responsibilities.
Table of Contents
As a legally binding document, it helps resolve disputes and ensures the shipment matches the listed details for smooth delivery.
How a Bill of Lading Is Used
A bill of lading is issued to the shipper once the goods are loaded onto the carrier’s vessel or vehicle. It travels with the cargo and is presented at the destination so the consignee can claim the goods. It also serves as a document of title, allowing ownership to transfer from the shipper to the consignee.
This ensures all parties understand the shipment details and terms throughout the journey.
Why is The Bill of Lading Important?
The bill of lading plays a crucial role in the shipping and logistics industry for several reasons.
1. The Proof of Shipment
As a receipt of goods, the bill of lading proves that the carrier has received the cargo for transport. It records the shipment’s details, including the type, quantity, and condition of the goods. In case of disputes or discrepancies, it serves as evidence to confirm the shipment’s contents and the agreement between the shipper and carrier.
2. The Contractual Agreement
One of the main roles of the bill of lading is to define the shipment’s terms and conditions. It acts as a contract between the shipper and the carrier, outlining each party’s responsibilities during transport. The details in the bill are legally binding and must be followed to ensure a smooth and successful delivery.
3. The Document of Title
By acting as a document of title, the bill of lading enables the transfer of ownership of the goods from the shipper to the consignee. This transfer of ownership is essential for the consignee to claim and take possession of the goods upon delivery. The bill of lading serves as a legal document that validates the consignee’s right to receive the goods and confirms their ownership once the cargo reaches its destination.
4. The Legal Framework
From a legal standpoint, the bill of lading sets a framework for the shipment that is recognized and enforceable by law. It defines the rights and obligations of all parties involved in the transportation process and serves as a key reference in disputes or claims. The information it contains is essential for regulatory compliance and supports transparency in the shipping and logistics industry.
Type of Bill of Lading
There are several types of bills of lading commonly used in the shipping industry.
1. Straight Bill of Lading
A straight bill of lading is a non-negotiable document used when goods are prepaid or shipped to a specific consignee. It directs the carrier to deliver the goods only to the named recipient and cannot be transferred to another party. This type of bill offers a simple way to ship goods directly to the intended recipient without requiring further documentation or endorsement.
2. Order Bill of Lading
An order bill of lading is a negotiable document that can be transferred to a third party through endorsement. It offers greater flexibility by allowing ownership of the goods to change hands during transit. This type of bill is often used when the consignee may not be the final recipient, making it easier to transfer ownership along the supply chain.
3. Bearer Bill of Lading
A bearer bill of lading, like an order bill, allows the transfer of ownership but doesn’t require endorsement. Ownership passes simply by presenting the document, making it useful in situations involving multiple parties or when quick transfer is needed. This type of bill is considered more flexible but also requires careful handling to maintain security.
4. Master Bill of Lading
A master bill of lading is issued by an ocean carrier to a freight forwarder or NVOCC for a consolidated shipment. It acts as the contract of carriage between the ocean carrier and the freight forwarder, detailing the terms of transport. Used when multiple shipments are combined into one container, it helps manage and track goods efficiently while ensuring each shipment is properly documented.
5. Air Waybill
An air waybill is a bill of lading issued by an airline for transporting goods by air. It serves as a contract of carriage between the shipper and the airline, outlining the terms of the shipment. This document is essential for air freight, as it provides key details about the cargo and supports smooth movement through the airline’s network.
6. Inland Bill of Lading
An inland bill of lading is used for domestic shipments transported by road or rail within a single country. It acts as both a receipt of goods and a contract of carriage between the shipper and carrier. This document is essential for tracking cargo movement and ensuring that goods reach their destination safely and on time.
7. Multimodal Bill of Lading
A multimodal bill of lading is a single document that covers the transportation of goods using multiple modes, such as sea, air, road, and rail. It acts as one contract of carriage for the entire journey, offering a streamlined solution for complex shipments. By combining all transport details into one document, it simplifies the shipping process and eliminates the need for separate contracts and paperwork.
8. Express Bill of Lading
An express bill of lading is a digital document sent quickly and securely to speed up the shipping process. It removes the need for physical paperwork, enabling faster handling of shipping documentation. This type of bill is often used for time-sensitive shipments where efficiency and quick delivery are crucial.
9. Through Bill of Lading
A through bill of lading is used when goods are transported by multiple carriers and modes to reach their final destination. It serves as a single document covering the entire journey from origin to delivery. This type of bill simplifies complex logistics by ensuring all parties involved understand the shipment’s details and their responsibilities.
What Information is in The Bill of Lading?
1. Shipper and Consignee Details
One of the main sections of the bill of lading lists the names and addresses of the shipper and consignee. This information identifies who is sending and receiving the goods. The shipper’s details show the origin of the shipment, while the consignee’s details indicate the delivery destination.
2. Description of Goods
The bill of lading includes a detailed description of the goods, such as their type, quantity, weight, and dimensions. This information helps carriers and consignees identify and handle the shipment properly. An accurate description ensures the correct items are delivered to the consignee in good condition.
3. Destination and Delivery Instructions
The bill of lading includes the final destination of the goods and any special delivery instructions. This section outlines where the cargo should be delivered and notes any specific requirements for the delivery. Clear instructions help carriers and consignees coordinate effectively to ensure timely and proper delivery.
4. Freight Charges and Payment Terms
Another key part of the bill of lading is the section on freight charges and payment terms. It details the shipping costs and identifies who is responsible for payment. Terms like pre-paid, collect, or third-party billing clarify how the charges will be handled, ensuring both parties understand and agree on the financial terms of the shipment.
5. Special Instructions and Handling Requirements
The bill of lading may also include special instructions and handling requirements to guide the transport of specific goods. This section outlines needs such as temperature control, handling of fragile items, or hazardous material regulations. Including these details helps ensure the goods are transported safely and in full compliance with applicable rules.
6. Insurance Coverage and Liability Terms
Insurance coverage and liability terms in the bill of lading define the carrier’s responsibility for the goods during transport. This section outlines the insurance in place and explains what happens in case of loss, damage, or delay. Understanding these terms is essential for both shippers and carriers to manage risks and ensure the goods are properly protected throughout the shipment.
7. Signatures and Dates
Signatures and dates play a critical role in validating the bill of lading and confirming the agreement between the shipper and carrier. The shipper, carrier, and consignee sign the bill of lading to show that they agree to the shipment’s terms and conditions and acknowledge receiving the goods. The dates on the bill of lading mark key points in the transportation process and help track the cargo’s movement from origin to destination.
When is a Bill of Lading Issued?
The carrier typically issues a bill of lading once they load the goods onto their vessel or vehicle. This document serves as a receipt for the goods and a contract between the shipper and carrier for transporting the cargo.
Issuing the bill of lading begins the shipping process and ensures that all parties understand the shipment details and their respective responsibilities.
Is a Bill of Lading Legally Binding?
Yes, a bill of lading is a legally binding document that serves as a contract between the shipper and carrier for the transportation of goods. The details included in the bill of lading outline the terms and conditions of the shipment, including the responsibilities of each party, the description of the goods, and the delivery instructions.
By signing the bill of lading, both the shipper and carrier agree to adhere to the terms specified in the document, making it a legally enforceable agreement.
Is The Bill of Lading The Same as an Invoice?
No, a bill of lading is not the same as an invoice, although both documents are related to the transportation of goods. While a bill of lading serves as a receipt of goods, a contract between the shipper and carrier, and a document of title for the goods, an invoice is a request for payment for the transportation services provided.
The bill of lading and invoice play distinct roles in the shipping process and serve different purposes to ensure the successful completion of the shipment.
How to Manage Bills of Lading
Managing bills of lading effectively is essential for ensuring the smooth and successful transportation of goods from origin to destination. Follow our tips:
1. Organize Documents
Organizing and easily accessing bills of lading is crucial for efficient shipping operations. Shippers and carriers should create a system to store and categorize bills of lading—whether in physical or electronic format—to allow quick retrieval and reference. When they organize documents systematically, they can track shipments, resolve discrepancies, and maintain accurate records of the transported goods.
2. Double-Check Details
Shippers and carriers must ensure all details in the bill of lading are accurate to prevent errors and delays in the shipping process. Before issuing the document, they should carefully review the description of the goods, shipping instructions, and payment terms to confirm everything matches the shipment requirements. By double-checking the information, they minimize the risk of mistakes and ensure the cargo is transported correctly and in compliance with regulations.
3. Track Shipments
Shippers and carriers use tracking systems and technologies to monitor shipment status as a key part of effective bill of lading management. By implementing tracking tools that provide real-time updates on the cargo’s location and condition, they gain better visibility and control over the transportation process. Tracking shipments helps them anticipate potential issues, address delays proactively, and communicate clearly with customers to ensure timely delivery.
4. Resolve Discrepancies Promptly
When discrepancies or issues arise with bills of lading, shippers and carriers must address them promptly and work together to prevent disruptions in the shipping process. They should establish clear procedures to resolve problems like incorrect information, damaged goods, or missing documentation, ensuring that shipments stay on track. By handling discrepancies quickly and transparently, they maintain trust, uphold accountability, and ensure the safe and efficient delivery of goods.
5. Implement Automation and Integration
Shippers and carriers can streamline shipping operations by automating and integrating bill of lading processes. By using digital solutions and software platforms, they can automate the generation, transmission, and processing of bills of lading, reducing manual errors and speeding up document handling. When they integrate these systems with other logistics tools, they further optimize the shipping process, improve communication, and gain better visibility and control over shipments.
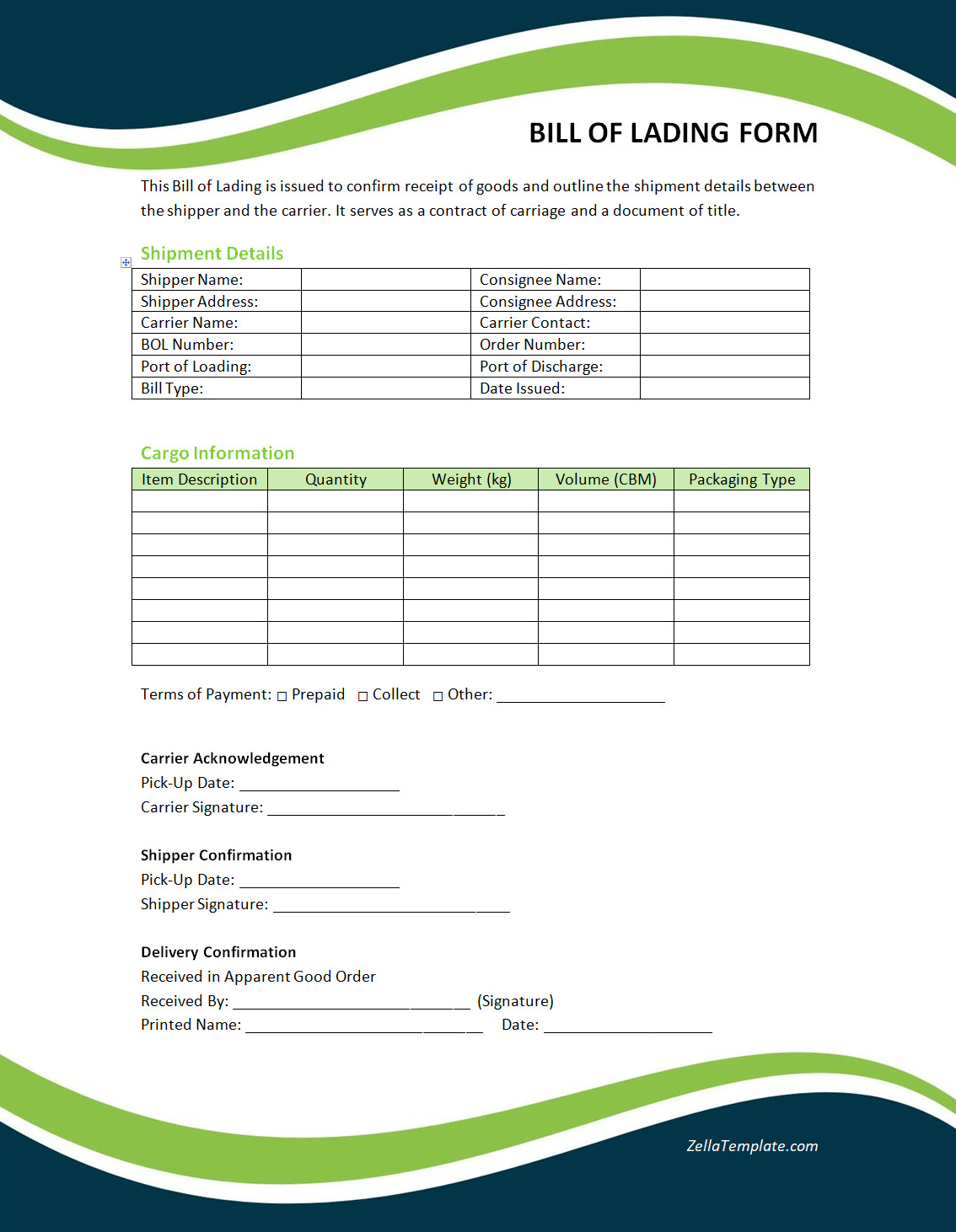
Bill of Lading Form Template
A bill of lading (BOL) form is a critical document for shipping and logistics, serving as a contract, receipt, and title of goods all in one. It ensures transparency, accuracy, and accountability between shippers, carriers, and receivers.
Use our free bill of lading form template today to streamline your shipping process and maintain professional documentation. Fully customizable and easy to use—perfect for freight companies, suppliers, retailers, and logistics professionals.
Bill of Lading Form Template – Word