Table of Contents
What Is a Bill of Materials (BOM)?
A Bill of Materials, commonly known as a BOM, is a vital document in the manufacturing industry that serves as a detailed roadmap for production processes. It is essentially a structured list that outlines all the raw materials, components, sub-assemblies, and quantities required to build a product.
Think of it as a recipe that guides manufacturers through the entire production process, ensuring that all necessary ingredients are in place before the final product is assembled.
What Is the Purpose of a BOM?
1. Ensuring Product Quality and Consistency
One of the key purposes of a BOM is to maintain product quality and consistency throughout the manufacturing process. By clearly defining the components and materials required for each product, manufacturers can ensure that every unit meets the specified standards and specifications. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also builds a reputation for reliability and excellence in the market.
It also facilitates smoother communication between departments—such as engineering, procurement, and production—by providing a single, authoritative source of information. This unified reference minimizes errors, speeds up decision-making, and allows teams to work in sync toward delivering high-quality products that meet both design standards and customer expectations.
2. Optimizing Production Efficiency
Another important purpose of a BOM is to optimize production efficiency and resource utilization. By providing a clear roadmap of all the materials and components needed for production, a BOM helps manufacturers plan their operations more effectively, minimizing waste and maximizing productivity. This optimized approach not only reduces production costs but also improves lead times and overall operational efficiency.
Furthermore, a detailed BOM allows manufacturers to identify opportunities for process improvement and optimization. By analyzing the components and quantities listed in the BOM, manufacturers can streamline their supply chain, identify cost-saving measures, and enhance their overall competitiveness in the market. This continuous improvement mindset is essential for sustainable growth and success in the manufacturing industry.
Why Use a BOM?
1. Enhanced Visibility and Control
One of the key reasons to use a BOM is to gain enhanced visibility and control over the production process. With a well-structured BOM in place, manufacturers have a clear understanding of all the components and materials required for each product, enabling them to track and monitor every step of the assembly process. This level of visibility allows for better decision-making, improved resource allocation, and proactive management of potential bottlenecks or issues.
Furthermore, a comprehensive BOM system provides greater control over inventory management and procurement processes. By accurately specifying the quantities and types of materials needed, manufacturers can avoid overstock or stockouts, minimize carrying costs, and optimize their supply chain operations. This level of control not only reduces operational risks but also improves financial performance and profitability.
2. Streamlined Collaboration and Communication
Another key benefit of using a BOM is the ability to streamline collaboration and communication among different teams within an organization. With a centralized source of information that outlines all the product specifications and requirements, teams such as design, engineering, procurement, and production can work more cohesively and efficiently. This seamless collaboration leads to better decision-making, reduced errors, and faster time-to-market for new products.
Moreover, a well-designed BOM system enables real-time updates and version control, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the latest information and revisions. This level of communication and transparency fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the organization, driving operational excellence and sustainable growth. By using a BOM as a common reference point, teams can align their efforts and resources towards achieving common goals and objectives.
Common Types of Bills of Materials (BOM)
In the manufacturing industry, different types of Bills of Materials are used to cater to the specific needs of various products and production processes. Every kind of BOM serves a distinct purpose and provides valuable insights into the components and materials required for production.
Let’s explore some common types of BOMs and their significance in the manufacturing landscape.
1. Engineering BOM
An Engineering BOM (EBOM) details a product’s technical specifications and requirements for each component. Used during the design phase, it defines the product structure, identifies critical parts, and shows functional relationships. It serves as a blueprint for design and development teams when creating prototypes and test models before full production.
The EBOM also ensures product integrity and compliance with regulations. By outlining each component’s technical characteristics, engineers can confirm the product meets performance, safety, and quality standards—essential in industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
2. Manufacturing BOM
A Manufacturing BOM (MBOM) focuses on production, listing the materials, quantities, and instructions needed to build the final product. Used on the shop floor, it guides workers through assembly with details like part numbers, descriptions, and step-by-step processes.
The MBOM also improves efficiency by specifying exact components, streamlining assembly, reducing waste, and maximizing resource use. This approach shortens lead times, lowers costs, and boosts productivity, enhancing both competitiveness and profitability.
3. Service BOM
A Service BOM lists the components, parts, and tools needed to service or repair a product. It supports after-sales maintenance by giving technicians clear instructions and replacement part details, helping reduce downtime and resolve issues quickly.
It also aids in managing spare parts inventory and service logistics by specifying exact components for different product variants. This ensures service centers are well-stocked, improves efficiency, cuts costs, and enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Who Prepares a Bill of Materials?
Creating a Bill of Materials (BOM) is a collaborative process involving several teams. While design and engineering teams prepare the initial BOM, procurement, production, and quality control teams provide vital input to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Design Team. Defines product specifications and lists required components, materials, and technical details. Works with engineers to ensure feasibility and updates the BOM as designs evolve.
- Engineering Team. Converts design specs into detailed requirements, ensuring components meet standards and regulations. Collaborates with production to optimize manufacturing processes.
- Procurement Team. Sources and purchases BOM materials, manages supplier relationships, negotiates contracts, and ensures timely delivery at competitive prices.
- Production Team. Builds the product following the BOM instructions. Coordinates with engineering and quality control to meet standards and production schedules.
- Quality Control Team. Ensures all materials and components meet quality and regulatory standards. Conducts inspections and tests, addressing any issues found.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration. Regular communication between teams ensures the BOM is accurate, complete, and aligned with production needs, improving efficiency and product quality.
Components of a Bill of Materials (BOM)
A typical Bill of Materials consists of several key components that provide detailed information about the materials, components, and specifications required to build a product. Let’s explore the essential components of a BOM and their significance in the manufacturing process.
1. Item Number
Each component or material listed in the BOM is assigned a unique item number for identification and reference purposes. The item number helps manufacturers track and locate specific components during the assembly process, ensuring that the right items are used in the right quantities. This numbering system also facilitates inventory management, procurement, and quality control activities by providing a standardized way to categorize and organize components.
2. Description
This information minimizes the risk of misunderstandings or errors, supports clear communication across departments, and helps maintain consistency in product quality. Detailed descriptions also assist in troubleshooting, repairs, and future product modifications by providing a clear record of the component’s role and attributes.
3. Quantity
The quantity of each component required for building the product is specified in the BOM to ensure accurate resource planning and procurement. By outlining the exact quantities needed for each item, manufacturers can avoid overstock or stockout situations, optimize resource utilization, and minimize waste. The quantity information also helps production teams plan their assembly processes and schedule production activities based on the availability of materials.
4. Unit of Measure
The unit of measure specifies the standard unit used to quantify the quantity of each component in the BOM. Common units of measure include pieces, kilograms, meters, liters, etc. By specifying the unit of measure for each component, manufacturers can ensure consistency and accuracy in quantifying materials across different products and production lines. This standardization helps streamline procurement, inventory management, and production planning activities.
5. Reference Designators
Reference designators indicate the specific locations or reference points where each component is to be installed in the final product. This information helps production workers identify the placement of each component during the assembly process, ensuring that all components are positioned correctly according to the design specifications. Reference designators also assist quality control specialists in verifying the completeness and accuracy of the assembly, reducing the risk of errors or omissions during production.
6. Vendor Information
Vendor information includes details of the suppliers or vendors from whom the components will be procured. This information helps procurement teams identify the source of each component, track supplier performance, and manage supplier relationships effectively. By specifying vendor information in the BOM, manufacturers can ensure timely delivery of quality materials, negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, and mitigate supply chain risks. This transparency and visibility into the supply chain enhance procurement efficiency and reliability, reducing lead times and production costs.
How to Create a Bill of Materials
Creating a comprehensive and accurate Bill of Materials requires careful planning, collaboration, and attention to detail. Let’s explore some key steps and best practices for creating a BOM that meets the specific requirements of your organization and product.
1. Gather Information
The first step in creating a BOM is to gather all the necessary information related to the product specifications, components, materials, and quantities required for production. This information can be sourced from design documents, engineering drawings, supplier catalogs, and other relevant sources. Ensure that all stakeholders are involved in the information-gathering process to capture a complete and accurate picture of the product requirements.
2. Organize Components
Once you have gathered all the necessary information, organize the components in a logical order based on their relationships and dependencies. Group components by sub-assemblies, categories, or production stages to create a structured and easy-to-follow BOM. This organization helps streamline the assembly process, improve production efficiency, and ensure that all components are accounted for during production.
3. Assign Item Numbers
Assign unique item numbers to each component listed in the BOM for easy identification and reference. Item numbers help track and locate specific components during production, procurement, and inventory management activities. Use a consistent numbering system that aligns with your organization’s standards and conventions to ensure clarity and accuracy in identifying components across different products and projects.
4. Verify Accuracy
Double-check the BOM for accuracy, completeness, and consistency before finalizing it for production use. Verify that all components are listed correctly, quantities are accurate, and specifications match the design requirements. Engage cross-functional teams to review the BOM for potential errors or discrepancies and address any issues proactively. Regularly update the BOM as product designs evolve or new components are introduced to maintain its accuracy and relevance.
5. Update as Needed
Regularly update the BOM as product designs evolve, components change, or new features are introduced. Ensure that the BOM reflects the latest design revisions, specifications, and requirements to avoid production delays or errors. Collaborate with design, engineering, and production teams to incorporate changes and updates to the BOM on time. By keeping the BOM up-to-date, you can ensure that all stakeholders have access to the most current information needed for successful production operations.
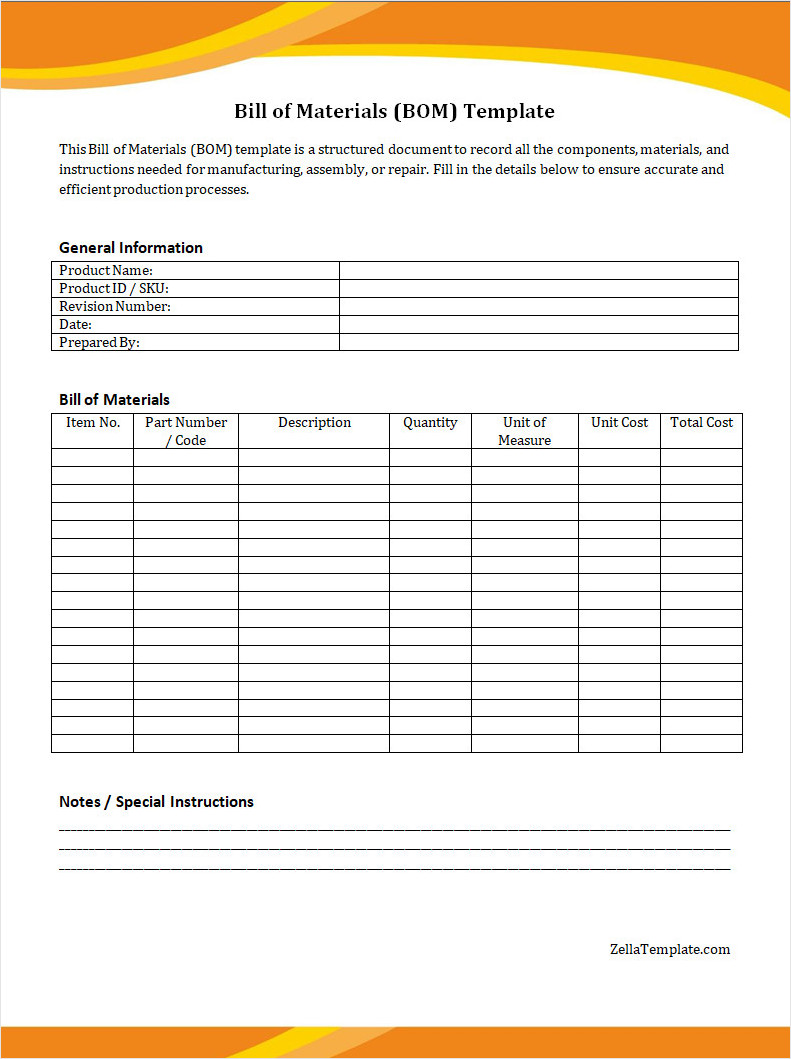
Bill of Material Template
Start using our free bill of materials template today to list components accurately, streamline production processes, and ensure efficient project planning and execution.
Bill of Material Template – Word